For loops
Estimated Time: 1 hour
We often want code to run again and again, until it’s time to stop. We learned that a while loop is a great tool when you know the stopping condition.
In this section we will explore a second tool for repeating code: the for loop. A for loop is a good fit when we want to run a block of code a definite number of times, or when we want to iterate over list of things.
for Loops
for loops step through a list of items in order. Each iteration will assign the next item to the loop variable, then execute the loop body.
The syntax of a for loop starts with the for keyword, and has an indented loop body. A for loop has a variable name, the in keyword, and a list of things to loop through.
for variable in items:
loop body to execute
The flow chart of a for loop is:
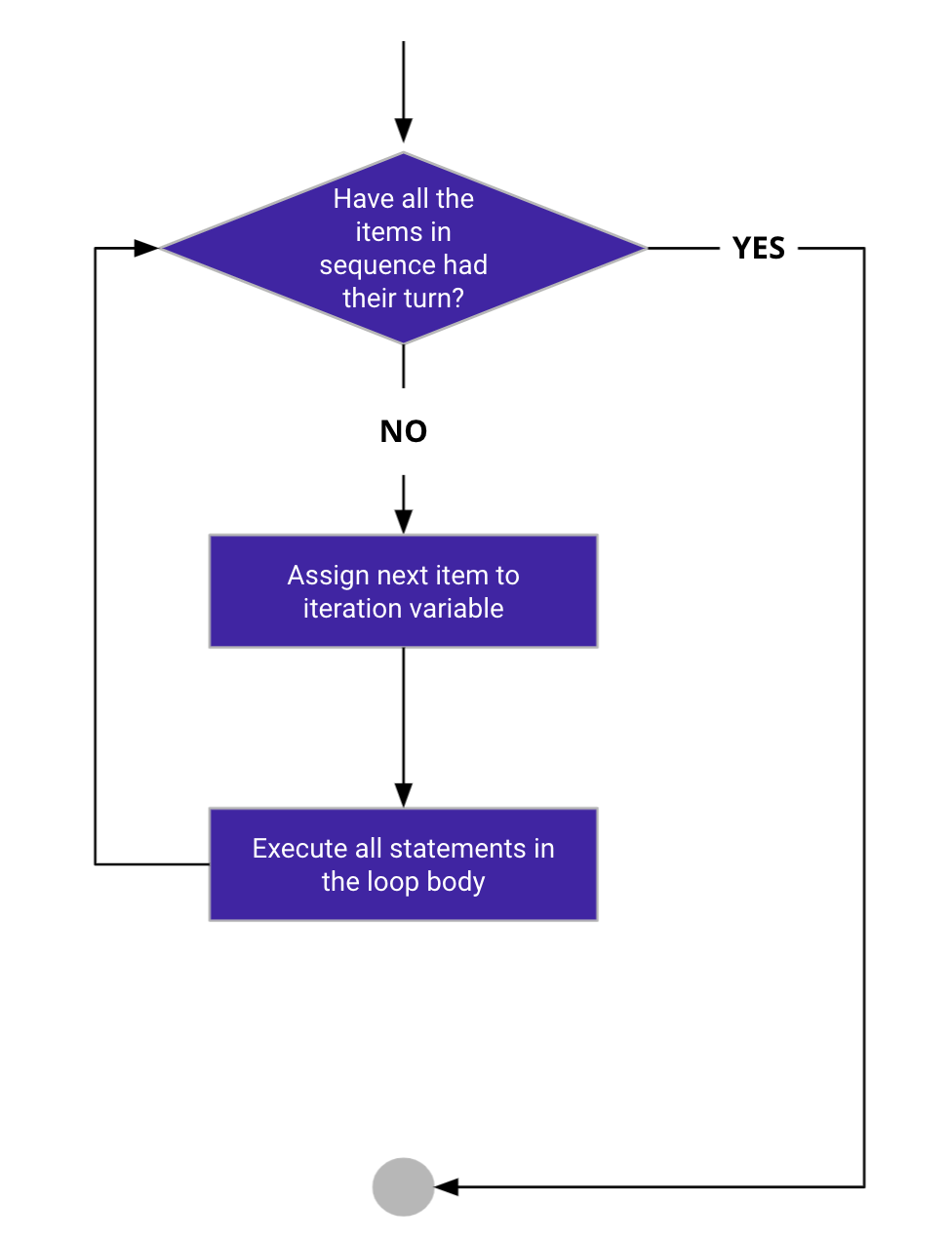
Let's take a look at an example of a for loop:
for i in [5, 4, 3, 2, 1] :
print(i)
print('Blastoff!')
This for loop will have the same output as the while loop we saw in the previous section:
5
4
3
2
1
Blastoff!
Let’s compare the for loop with the while loop :
for i in [5, 4, 3, 2, 1] :
print(i)
print('Blastoff!')
n = 5
while n > 0:
print(n)
n = n - 1
print('Blastoff!')
🤔 Compare the two code examples above (the for loop and the while loop). What do you notice about them?
while vs. for
Similarities:
- loop keyword, then something, then
: - loop body is indented
Differences:
- variable
ncreated before the while loop, variableicreated as part of theforloop whileloop changes the variable withn = n - 1,forloop variable changes automaticallyforloop has to write out exactly what numbers to loop through
for loop iteration variable
The initial statement in the for loop is:
for i in [5,4,3,2,1]:
In this code, the loop creates a new variable i. The value of i will change in each iteration of the loop, to take on the value of each item in the list. In this example, i will take on successive values of 5, 4, 3, 2, and 1.
As you can see, for loops offer a more direct syntax than while loops, because you can explicitly declare the values of the iteration variable.
We’ll cover the list syntax [5, 4, 3, 2, 1] in more detail later in the course. For now, you can use it to write for loops, without knowing exactly what it means. You can put any values inside the [], and the loop variable will be assigned to each value in turn.