Foreign Keys and JOINS
Foreign keys and JOINs are the basic SQL tools for creating and using relationships between tables.
A foreign key is a unique identifier that will allow to reference of one record into a another table.
Let's take the following example, let's say we have a database of customers and orders.
To connect the information of one Order to one Customer (an order that included a chair and belongs to a customer named Sally) you will need a unique identifier for both: Order and Customer. Those numbers help to make the connection between information across different tables. It looks like this:
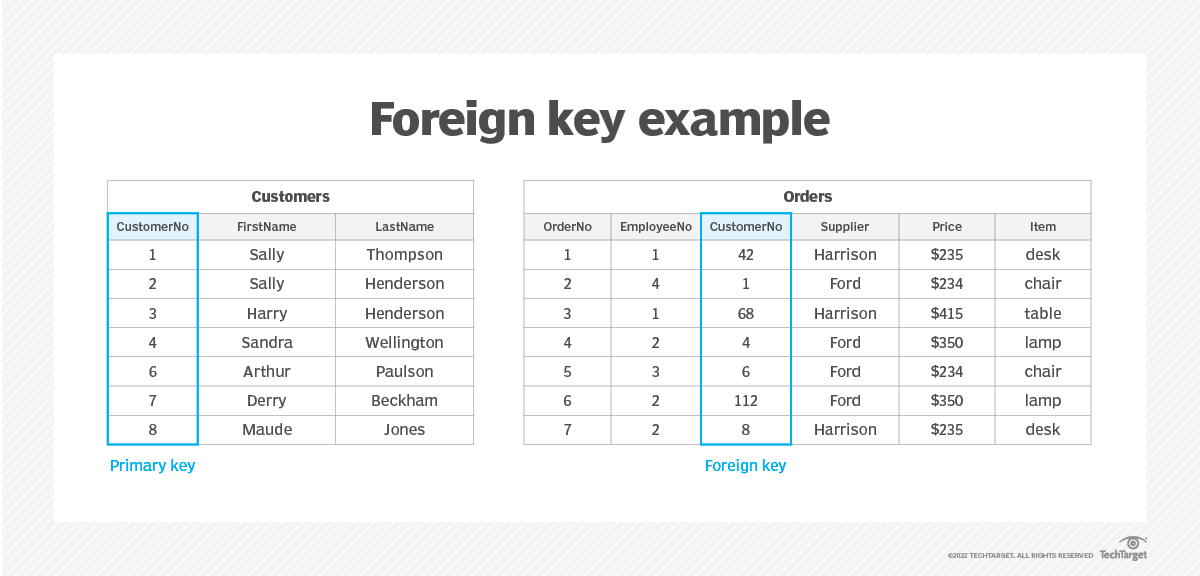
As you can see in the table Customers, Customer No 1 is Sally Thompson. Now to table Orders, Customer 1, made an order for a chair (Order No 2).
Video: Linking Tables with Keys
This video illustrates linking the Primary key of one table with the Foreign key of another table:
FOREIGN KEY
As we saw just before, Foreign keys are a way of linking data in two different tables in a relational database. They are used to establish a relationship between two tables, where the values in one table depend on the values in another table.
A foreign key is a column or set of columns in one table that refer to the primary key of another table. The purpose of a foreign key is to ensure data integrity, which means that the data in the database is consistent and accurate.
For example, consider a database that has two tables: a customers table and an orders table. The customers table contains information about customers, including a unique identifier for each customer, which is the primary key. The orders table contains information about the orders placed by each customer, including the customer's identifier.
CREATE TABLE customers (
id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY AUTOINCREMENT,
name TEXT NOT NULL,
email TEXT NOT NULL UNIQUE
);
CREATE TABLE orders (
id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY AUTOINCREMENT,
customer_id INTEGER NOT NULL,
product TEXT NOT NULL,
quantity INTEGER NOT NULL,
FOREIGN KEY (customer_id) REFERENCES customers (id)
);
The customer_id column in the orders table is a foreign key. It refers to the primary key of the customers table. It tells us which customer the order belongs to.
The FOREIGN KEY statement is a database constraint. It creates a relationship between the two tables, where each order in the orders table must correspond to a customer in the customers table. If you try to insert an order into the orders table with a customer_id that doesn't exist in the customers table, you'll get an error.