JOINS
The SQL JOIN statement is used to combine rows from two or more tables based on a related column between them.
Here's an example of a JOIN statement:
SELECT customers.name, orders.product
FROM customers
JOIN orders
ON customers.id = orders.customer_id;
The JOIN statement combines the rows from the customers and orders tables based on the customer_id column. The result of this query contains the name from the customers table and product from the orders table, with each row representing a customer and their corresponding order.
If a customer has multiple orders, each order will appear as a separate row in the results.
Practice: Writing JOINs
Practice JOINs on SQLBolt
SQL Lesson 6: Multi-table queries with JOINs
Other kinds of JOIN
The most common kind of JOIN is the INNER JOIN. If you don't specify another kind of join, it will treated as an INNER JOIN.
There are several types of JOIN statements in SQL, each of which returns different subsets of the data from the joined tables.
INNER JOINLEFT JOINRIGHT JOINFULL OUTER JOIN
The names correspond to the portions of a Venn diagram of the tables:
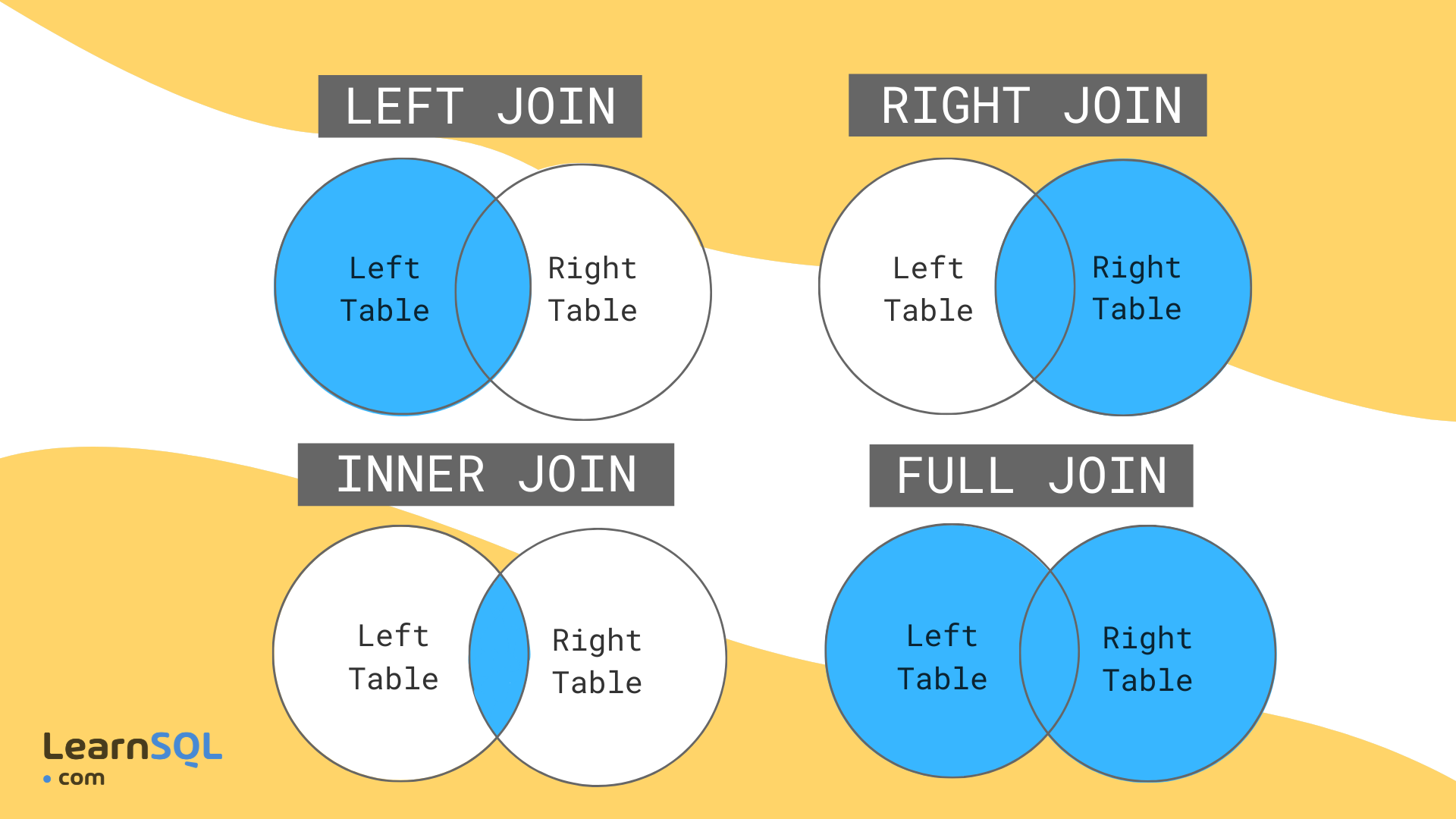
An INNER JOIN returns only the rows that have matching values in both tables.
The other three joins are all 'outer' joins in some sense, since they include 'outer' values (not just inner ones).
A LEFT JOIN returns all the rows from the left table and the matching rows from the right table. If there is no matching row in the right table, the result will contain NULL values for the columns from the right table.
A RIGHT JOIN is similar to a LEFT JOIN, but it returns all the rows from the right table and the matching rows from the left table.
A FULL JOIN returns all the rows from both tables, including the rows that have no matching values in either table.
You'll almost exclusively use the INNER JOIN (or just JOIN), but occasionally a LEFT or RIGHT JOIN will be helpful. FULL JOIN is pretty rare, so you'll probably only see it in tutorials.
Practice: Outer joins
Practice OUTER JOINs on SQLBolt: