Agile Software Development
Estimated Time: 30 minutes

We began this with an assertion that software is a team sport!
Even though there can be some friction (remember the image above?), building great products requires collaboration and engagement with users and team members. In this lesson, we explore how agile development helps software teams collaborate well.
What is Agile?
Agile software development is an approach to software development that emphasizes building and shipping small pieces of working functionality.
Key Learnings
-
Agile development is an iterative approach to software development. Agile teams focus on delivering a working product incrementally. They value collaboration, flexibility, and rapid iteration.
-
Agile is so popular that there is an "agile manifesto" which describes its core principles including:
- Individuals and interactions over processes and tools
- Working software over comprehensive documentation
- Customer collaboration over contract negotiation
- Responding to change over following a plan
- Agile teams typically work in short cycles called sprints or iterations. Each sprint results in a working product, which the team uses to solicit feedback from stakeholders and to refine and plan the next sprint.
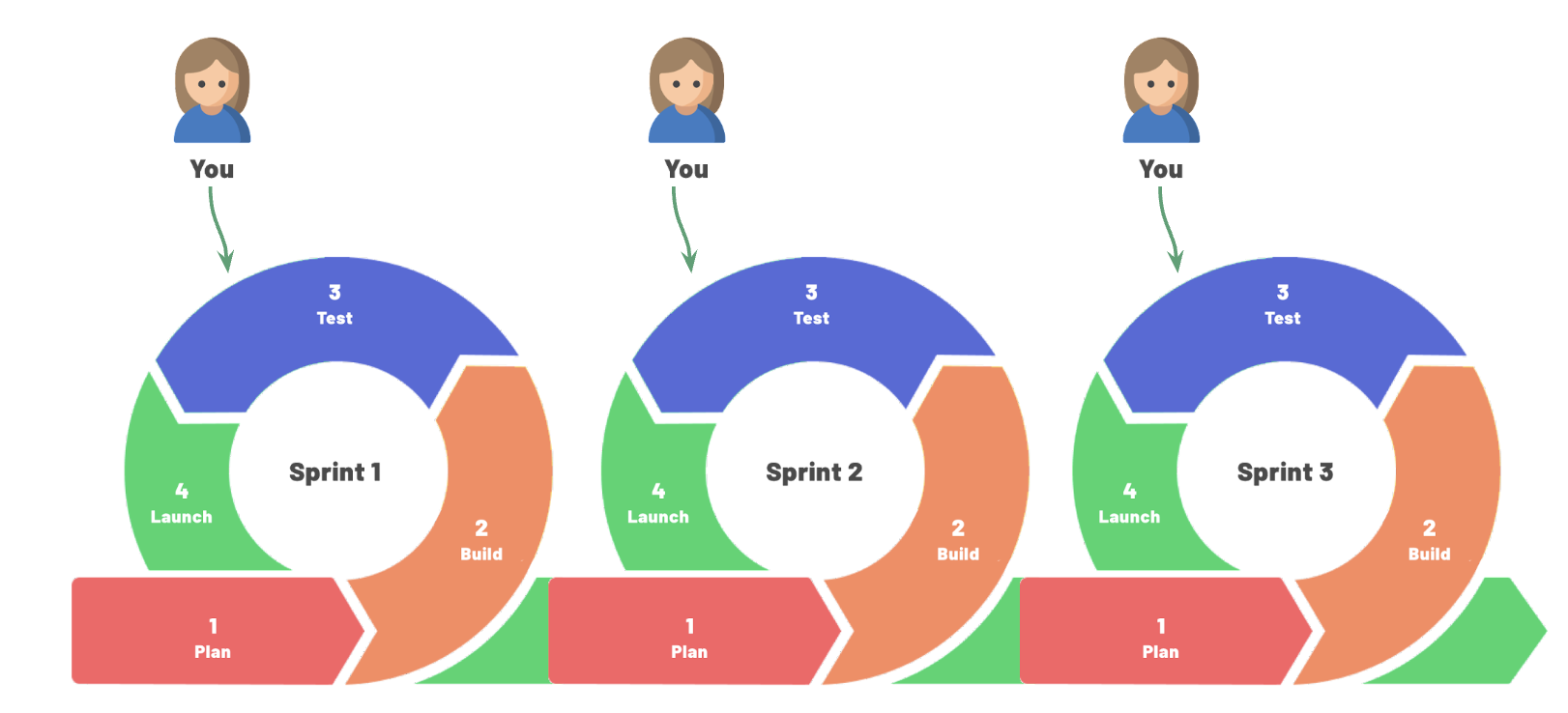
Why Iterative Development Matters
Iterative development is at the heart of agile and it helps to promote:
- Faster time-to-market: By delivering working products incrementally, agile teams can release products faster and get customer feedback sooner.
- Increased flexibility: Agile teams can respond to changing requirements and customer needs quickly, making it easier to pivot if necessary.
- Improved collaboration: Agile teams work closely together and with stakeholders throughout the development process, fostering collaboration and communication.
- Continuous improvement: Agile teams use feedback from stakeholders to continuously improve the product, resulting in a better end product.
Alternatives to Agile
While agile development is extremely popular, it's not the only option. One alternative to agile is waterfall development. Waterfall is a traditional project management approach that involves a linear sequence of phases, including planning, design, implementation, testing, and deployment. Each approach has its own advantages and disadvantages, and the best approach for a given project depends on various factors such as project scope, team size, and available resources.
Agile sprints
An agile sprint is a short, focused period of development that typically lasts 1-4 weeks. During a sprint, the development team works to deliver a specific set of features or functionalities. The sprint begins with a sprint planning meeting, where the team reviews the backlog of user stories and selects the stories that they will work on during the sprint.
User stories are a critical part of the sprint planning process. User stories describe a specific feature or functionality from the perspective of the user or customer. They typically follow a simple format: "As a [user], I want to [do something], so that I can [achieve a goal]." User stories help to define the scope of the work to be done during the sprint and ensure that the team is working on features that are valuable to the customer. Some examples include:
- As a logged-in user, I want to update my profile so that my information is complete
- As a student, I want to see a list of all assignments and due dates, so that I know what to work on next
Steps of an agile sprint
-
Sprint planning: the team selects user stories to work on during the sprint, estimates the effort required, and determines how much work they can realistically complete.
-
Sprint execution: the team works together to develop and test the features outlined in the user stories. They hold daily stand-up meetings to discuss progress and any obstacles they are facing.
-
Sprint review: the team demonstrates the working software to stakeholders and receives feedback.
-
Sprint retrospective: the team holds a retrospective meeting to review the sprint, identify areas for improvement, and make changes to improve their process for the next sprint.
Roles in an agile sprint
Different team members contribute to the success of an agile sprint. Below is a summary of what various team members do during a sprint
Product Manager or Owner: defines and prioritizes the backlog of user stories, and ensures the team is working on features that deliver value
UX designer: create wireframes, prototypes, or other designs to guide development, and works with development team to ensure that the design is implemented correctly
Software engineers: build and deliver working software during the sprint, including coding, testing and deployment
Scrum Master: facilitates sprint planning and retrospective meetings, and helps the team to continuously improve their process. In some teams, the product manager or a senior engineer plays the role of scrum master
Stakeholders: Stakeholders are the people who will be using or affected by the software being developed. They provide feedback on the working software during the sprint review and may provide input on user stories during the sprint planning process.
Test your understanding
Complete the quiz below to test your understanding of agile development