Regression in ML
Imagine you are trying to predict the price of a house based on various features like the number of bedrooms, the area in square feet, and the age of the house. This problem cannot be solved with classification because the outcome you want to predict, i.e, the house price, is a continuous variable, meaning it can take ANY numerical value within a range.
In contrast, classification is only used when the outcome is a categorical variable with distinct categories, like predicting whether an email is spam or not.
Regression
However, unlike classification, the categories in regression are continuous values, such as height, weight, or price. Imagine you want to estimate how much time it will take for you to reach a friend's house based on the distance you have to travel and the average speed at which you drive.
In machine learning, regression works in a similar way. You show the computer many examples of distances traveled and the corresponding time taken to reach a destination. The computer then looks for patterns and relationships between the distances and the time.
Once the computer has learned from these examples, you can provide it with a new distance, and it will predict how much time it will take you to walk there based on what it learned. Hence, regression helps us make accurate predictions for numerical outcomes, just like estimating the time it will take for you to reach your friend's house based on the distance and your walking speed.
Linear regression
Linear regression is a statistical technique used in machine learning to model the relationship between a dependent variable (the outcome we want to predict) and one or more independent variables (features or factors that influence the outcome). It assumes that the relationship between the variables can be approximated by a straight line.
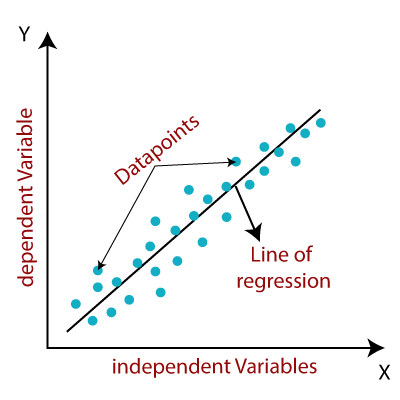
Imagine you have a dataset that includes information about several houses, such as the size of the house (in square feet), the number of bedrooms, and the age of the house. You also have the corresponding prices at which each house was sold.
Linear regression works by finding a straight line (a mathematical equation) that best fits the relationship between the features (size, bedrooms, age) and the house prices. The goal is to find a line that minimizes the difference between the actual house prices and the predicted prices given by the line.
Here is a code snippet of a linear regression model that predict the price of house using a simulated data. Play around with the new_house values and see how the predicted house price changes.
In the code snippet, we used the house_size, number_of_bedrooms, and year_built as the independent variable and house_price as the dependent variable. The model is trained on the data using model.fit(), and we use it to predict the price of a new house with a size of 1600 square feet, 3 bedrooms, and built year of 2008. The predicted_price will give us the estimated price for that new house based on the relationship learned from the training data.
👩🏾🎨 Practice: Regression in ML... 🎯
-
Which of the following statements best describes supervised learning in the context of regression?
- Supervised learning involves training a model with labeled data and then making predictions on unlabeled data.
- Supervised learning is a technique to train models only on numerical data.
- Supervised learning does not involve the use of any training data.
- Supervised learning is only used for classification problems.
-
Which of the following statements is true about linear regression?
- Linear regression is suitable only for categorical data.
- Linear regression assumes a linear relationship between dependent and independent variables.
- Linear regression does not involve any assumptions about the data.
- Linear regression can only predict binary outcomes.
➡️ Next, we'll look at
Unsupervised learning... 🎯